New Patients Are Welcome!
Defeating Gum Disease: Strategies for a Healthy Smile and Strong Gums
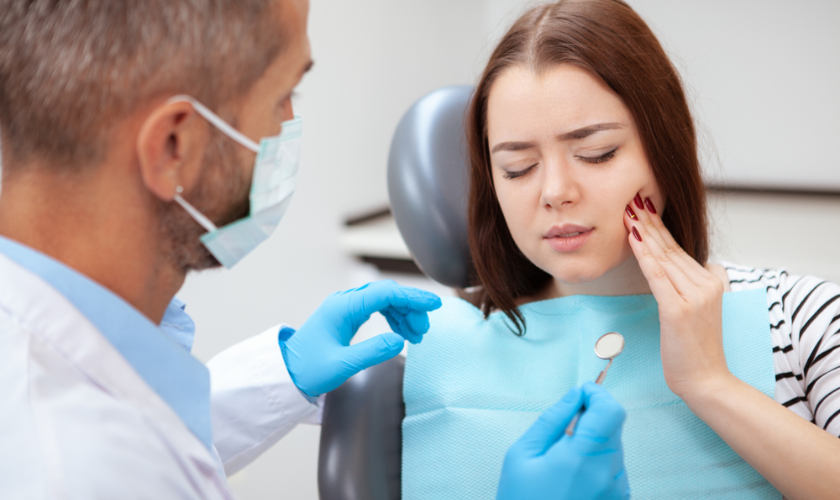
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to gum recession, tooth loss, and even systemic health issues. However, with the right strategies and preventive measures, you can defeat gum disease and maintain a healthy smile with strong gums. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease, as well as effective strategies for prevention and maintaining optimal gum health.
Understanding Gum Disease:
Causes: Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque buildup, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which can only be removed by a dental professional. The bacteria in plaque and tartar release toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and infection.
Symptoms: Early-stage gum disease, known as gingivitis, may present with symptoms such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, and gum sensitivity. As gum disease progresses to periodontitis, symptoms can include receding gums, loose teeth, pus between the teeth and gums, changes in bite, and the formation of deep pockets around the teeth. It’s important to seek professional dental care if you experience any of these symptoms.
Preventing Gum Disease:
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene: The foundation of gum disease prevention is maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist are essential for preventing gum disease. Professional dental cleanings can remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be eliminated through regular brushing and flossing. Additionally, your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide necessary treatment before it progresses.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can prevent gum disease. Avoid tobacco use, as smoking and chewing tobacco increase the risk of gum disease. Maintain a balanced diet that is low in sugar and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Adequate hydration and regular exercise also support overall oral and systemic health.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease:
Scaling and Root Planing: In cases of mild to moderate gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be recommended. This involves removing plaque and tartar from the surfaces of the teeth and the roots below the gumline. The root surfaces are then smoothed to promote gum reattachment and prevent further bacterial growth.
Antibiotic Therapy: Antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and inflammation associated with gum disease. They can be administered orally, topically (in gel form), or directly applied to the affected areas.
Surgical Interventions: In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical interventions may be necessary. Procedures such as gum grafting, flap surgery, and bone grafting can help restore gum tissue, reduce pocket depths, and promote gum and bone regeneration.
Maintaining Optimal Gum Health:
Stick to a Consistent Oral Care Routine: Consistency is key in maintaining healthy gums. Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time, and floss daily. Replace a toothbrush with soft bristles every three to four months. Consider using an electric toothbrush, which can be more effective in removing plaque.
Use Gum-Friendly Products: Opt for oral care products that are specifically designed for gum health. Look for toothpaste and mouthwash that are formulated to combat plaque and gingivitis. Consider using interdental brushes or water flossers to clean hard-to-reach areas between the teeth.
Monitor Your Gum Health: Pay attention to any changes in your gum health and seek professional dental care if you notice persistent gum inflammation, bleeding, or other concerning symptoms. Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to monitor your gum health and address any issues early on.
The Bottomline
Defeating gum disease requires a combination of effective preventive measures, professional dental care, and good oral hygiene practices. Adopting a proactive approach and implementing these strategies can protect your gums, maintain a healthy smile, and reduce the risk of gum disease-related complications. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy and beautiful smile.